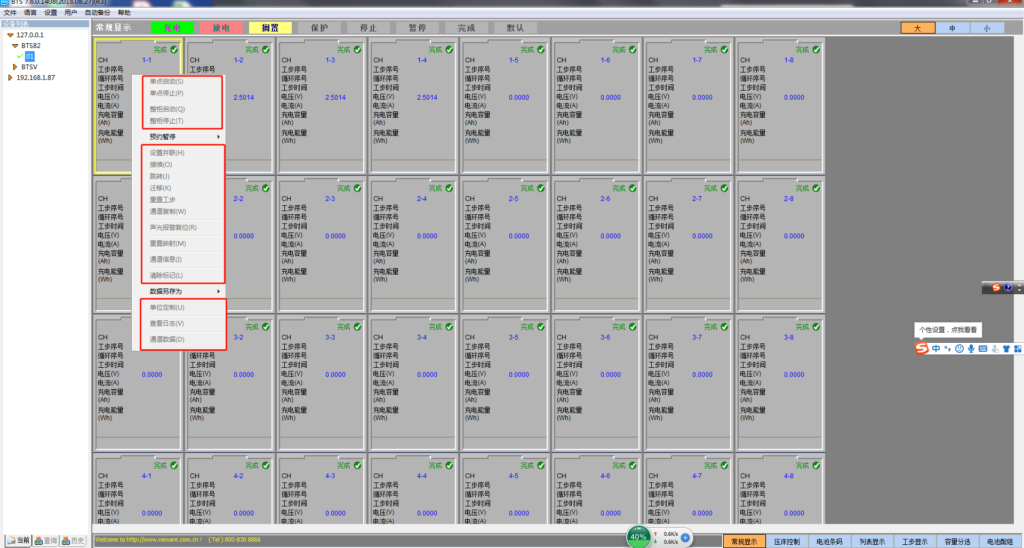
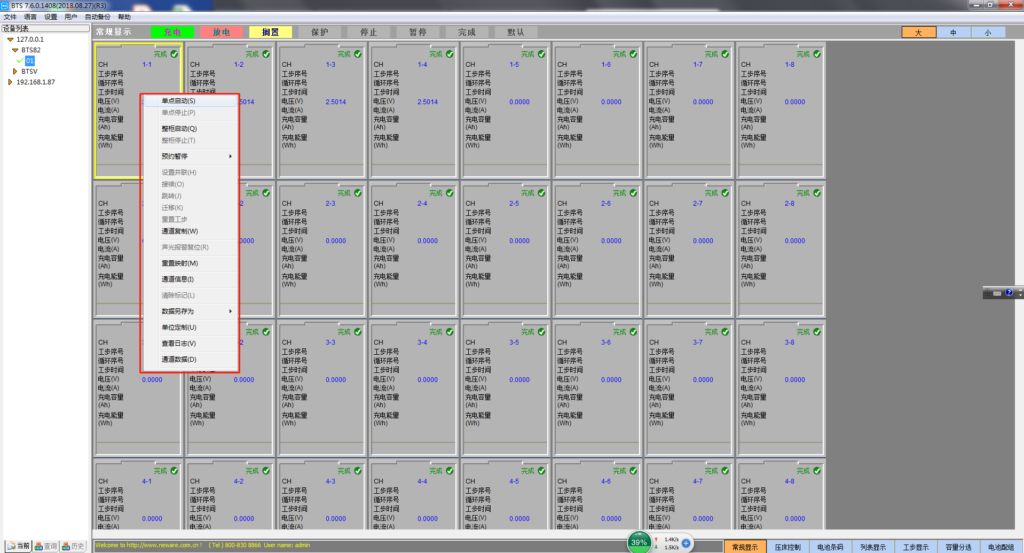
In the channel display area, right-click, if the following operations are gray (not operational), the user must log in first to perform the following operations. Single point start: The “Start” window consists of two sub-windows: “Standard step settings” and “Professional step settings”
- Single point start: The “Start” window consists of two sub-windows: “Standard step settings” and “Professional step settings”;
- Single point stop: For the running channel, when we want to reset the step of one or several channels or want to stop/pause the test, then the operation of the channel needs to be stopped;
- the whole cabinet starts: When we want to start all the available channels on a certain device, it is necessary to start the whole cabinet;
- Stopping the whole cabinet: Stop all the channels in certain equipment at the same time, that is, stop the whole cabinet;
- Appointment pause: When the user needs to pause after the current step/cycle is completed, or pause the specified step/cycle, pause the operation, which can be suspended by appointment;
- Set parallel connection: By setting the channels in parallel, the current range can be expanded, and four channels can be connected in parallel in maximum;
- Connection: The user can continue to the original unfinished test step for the “stop”/“pause” state or the “protected” state of the upper computer under power failure, effectively preventing the loss of measurement data;
- Jump: When the channel is executing the step, it can jump to the target step, which can maintain the normal connection of the test data;
- Migration: The process parameters and test data of an unfinished test channel are migrated to another finished test channel to continue the test. The purpose is to prevent the test from being interrupted due to channel damage and other factors, affecting the test;
- Reset step: When the user needs to modify the step or parameter of the running channel, it can be implemented by “reset step”;
- Channel copy: copy the step parameters of one channel to another channel or channels when the channel ranges are the same;
- sound and light alarm reset (R)
- Reset mapping (M): mapping all the channels corresponding to the lower computer, and also modifying the mapping;
- Channel information (I): Query channel information to know the details of the selected channel;
- Clear flag (L): For channels that are in the “non-completion” state and the “non-running” state, that is, channels that are in the states of “protection”, “stop”, “pause”, etc., they can be cleared. After that, it is changed to the “completed” state;
- Save the data as You can export the test data in the format of NDA file or Excel file, and customize the path to facilitate the user to view the data information.
- Unit customization (U): Set the corresponding unit parameters according to different test purposes of the user;
- View log (V): View all operations performed on the channel;
- Channel data (D): The channel data information can be viewed in real time.
If you have any other questions, please contact me with: nucky@newarebattery.com
Comments are closed.






